Software:- Software or application is a set of instructions or programs instructing a computer to do specific tasks.
Product: Application or Software created for multiple customer by keeping functionality in general for all. This can be used by anyone based on his or her business need. Example: MS Office, eclipse etc.
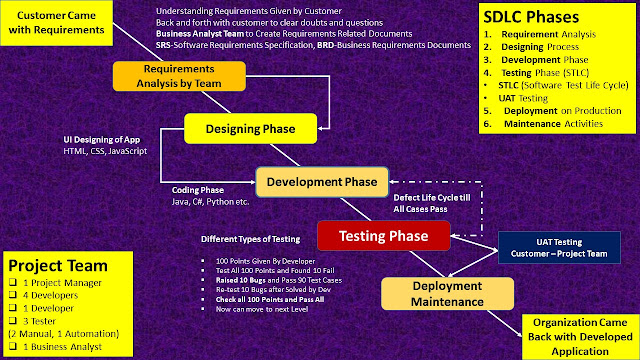
Stage 1: Planning and Requirement Analysis
Requirement analysis is the most important and fundamental stage in SDLC. It is performed by the senior members of the team with inputs from the customer, the sales department, market surveys and domain experts in the industry. This information is then used to plan the basic project approach and to conduct product feasibility study in the economical, operational and technical areas.
Stage 2: Defining Requirements
Once the requirement analysis is done the next step is to clearly define and document the product requirements and get them approved from the customer or the market analysts. This is done through an SRS (Software Requirement Specification) document which consists of all the product requirements to be designed and developed during the project life cycle.
Stage 3: Designing the Product Architecture
SRS is the reference for product architects to come out with the best architecture for the product to be developed. Based on the requirements specified in SRS, usually more than one design approach for the product architecture is proposed and documented in a DDS - Design Document Specification.
This DDS is reviewed by all the important stakeholders and based on various parameters as risk assessment, product robustness, design modularity, budget and time constraints, the best design approach is selected for the product.
Stage 4: Building or Developing the Product
In this stage of SDLC the actual development starts and the product is built. The programming code is generated as per DDS during this stage. If the design is performed in a detailed and organised manner, code generation can be accomplished without much hassle.
Stage 5: Testing the Product
This stage is usually a subset of all the stages as in the modern SDLC models, the testing activities are mostly involved in all the stages of SDLC. However, this stage refers to the testing only stage of the product where product defects are reported, tracked, fixed and retested, until the product reaches the quality standards defined in the SRS.
Different Level of Testing we do in this Phase:
Once the product is tested and ready to be deployed it is released formally in the appropriate market. Sometimes product deployment happens in stages as per the business strategy of that organisation. The product may first be released in a limited segment and tested in the real business environment (UAT- User acceptance testing). Then based on the feedback, the product may be released as it is or with suggested enhancements in the targeting market segment. After the product is released in the market, its maintenance is done for the existing customer base.
Type of Software
- System Software: - Drivers, Operating System etc.
- Programming Software:- Debugger, Compiler, Interpreter
- Application Software:- User Specific, Banking Software, Healthcare Software
Project & Product
Project:- Application or Software created specific to customer to achieve specific goal that we can consider as Project. A project is a temporary endeavour that is undertaken to create a unique product or service. It has fixed period to achieve. Example: In-House Attendance System.Product: Application or Software created for multiple customer by keeping functionality in general for all. This can be used by anyone based on his or her business need. Example: MS Office, eclipse etc.
Software Testing:-
Software testing is an activity to check whether the actual results match the expected results and to ensure that the software system is Defect free.
Quality:- Quality means anything, which satisfied business or individual need based on their function & features.
- Bug Free
- Easy to use
- Meet the exceptions
- Good Design and Functionality
- Reliable and Consistence
- Value of Money
Quality Standard: - ISO 9001, ISO 9004
ISO: International Standards Organisation
SDLC: - Software Development Life Cycle
SDLC is a process followed for a software project, within a software organisation. It consists of a detailed plan describing how to develop, maintain, replace and alter or enhance specific software. The life cycle defines a methodology for improving the quality of software and the overall development process.
SDLC is a process followed for a software project, within a software organisation. It consists of a detailed plan describing how to develop, maintain, replace and alter or enhance specific software. The life cycle defines a methodology for improving the quality of software and the overall development process.
Stage 1: Planning and Requirement Analysis
Requirement analysis is the most important and fundamental stage in SDLC. It is performed by the senior members of the team with inputs from the customer, the sales department, market surveys and domain experts in the industry. This information is then used to plan the basic project approach and to conduct product feasibility study in the economical, operational and technical areas.
Stage 2: Defining Requirements
Once the requirement analysis is done the next step is to clearly define and document the product requirements and get them approved from the customer or the market analysts. This is done through an SRS (Software Requirement Specification) document which consists of all the product requirements to be designed and developed during the project life cycle.
Stage 3: Designing the Product Architecture
SRS is the reference for product architects to come out with the best architecture for the product to be developed. Based on the requirements specified in SRS, usually more than one design approach for the product architecture is proposed and documented in a DDS - Design Document Specification.
This DDS is reviewed by all the important stakeholders and based on various parameters as risk assessment, product robustness, design modularity, budget and time constraints, the best design approach is selected for the product.
Stage 4: Building or Developing the Product
In this stage of SDLC the actual development starts and the product is built. The programming code is generated as per DDS during this stage. If the design is performed in a detailed and organised manner, code generation can be accomplished without much hassle.
Stage 5: Testing the Product
This stage is usually a subset of all the stages as in the modern SDLC models, the testing activities are mostly involved in all the stages of SDLC. However, this stage refers to the testing only stage of the product where product defects are reported, tracked, fixed and retested, until the product reaches the quality standards defined in the SRS.
Different Level of Testing we do in this Phase:
- Unit Testing
- Integration Testing
- System Testing
- UAT Testing
Once the product is tested and ready to be deployed it is released formally in the appropriate market. Sometimes product deployment happens in stages as per the business strategy of that organisation. The product may first be released in a limited segment and tested in the real business environment (UAT- User acceptance testing). Then based on the feedback, the product may be released as it is or with suggested enhancements in the targeting market segment. After the product is released in the market, its maintenance is done for the existing customer base.


No comments:
Post a Comment